|
Use the "Edit GCR" dialog to edit the GCR settings of a Black Generation Table. You can access this dialog by clicking Edit button from the Advanced Black Generation dialog (Figure 1).
The "Edit GCR" dialog uses three types of editing controls to set the GCR settings: Quick, Curves, and Traditional. Each method is a different way to edit the GCR information. Click the appropriate button at the top of the "Edit GCR" dialog to choose either [Quick], [Curves], or [Traditional]. You cannot use a combination of these methods; switching from one to another method will cause the previous changes to be lost.
 Quick Quick
The [Quick GCR] method uses two types of controls to change the GCR: Gray Level and Skeleton Black. When using the [Quick GCR] method, you cannot edit the lines on the graph directly, instead, changing the Gray Level and Skeleton Black curves changes the lines on the graph for you (Figure 1).
- Quick GCR (Gray Level)
- The Gray Level control specifies the ratio of primary black (K) and process black (CMY) from the 0% Gray Level to the beginning of the Skeleton Black transition point. If the Skeleton black amount is set to 70, then the Gray Level sets the K to CMY ratio from the 0% Gray Level to 30% (inverse of the 70% Skeleton black amount) Gray Level.
- Skeleton Black
- The Skeleton Black [Amount] determines the Gray Level percentage where the K to CMY ratio changes to a solid black. The solid black is set by the three radio buttons: Primary Black, CMY Black, and CMY and Primary Black. [Primary Black] only uses K for 100% Gray Level, [CMY Black] uses a CMY to create the 100% Gray Level, and [CMY and Primary Black] use 50% K and 50% CMY to reach the 100% Gray Level.
 Curves Curves
The Curves method allows you to edit the lines on the graph directly.
- Curve Type
- Select [Balance] to modify the K to CMY ratio of Gray Level percentages (Figure 3). [Additive] shows a blue line that specifies how much ink is to be added to ensure that process black (CMY) and primary black (K) are equally dark (Figure 4). This allows you to increase the saturation in dark regions, giving more depth to the color. The default for this curve is a flat line across the bottom of the graph. The [Additive] setting usually does not need to be adjusted.
- Edit Mode
- Select [Smooth] to draw the GCR values on the graph freehand with the mouse. Use [Line] to create the GCR values using line segments.
- Opacity
- The [Opacity] slider controls how opaque primary black is to be considered when converting CMYK files to RGB. It has no effect on RGB source files. The default Opacity is 255, and it generally should not be set lower than 230.
 Traditional Traditional
The Traditional method sets a more complicated type of GCR setting using different controls and curve types. The black line on the graph shows the GCR, and the blue line on the graph shows the Gray Balance (Figure 5).
- Black Start
- The [Black Start ]value controls the Gray Level percentage where K begins to be used.
- Total Black
- The [Total Black] setting controls how much K is used at the 100% Gray Level.
- Total Ink
- Use the[ Total Ink] value to limit the amount of total ink that is used (including all color channels). Modifying the [Total Ink] setting has more effect on the Gray Balance (blue line) than the GCR (black line).
- Black Curve Type - The [Black Curve Type] sets the type of curve used to add K to the GCR ratio of K and CMY. Changing this curve also modifies the Gray Balance (blue line).
Related Topics
|
Figure 1
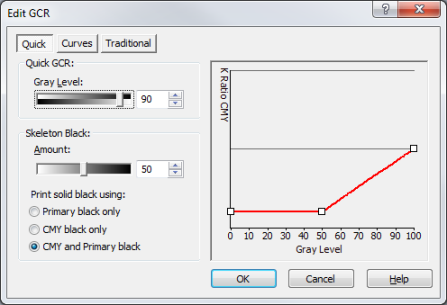
Figure 2
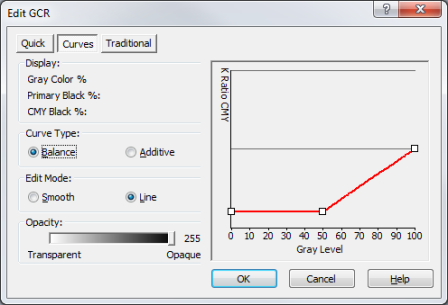
Figure 3
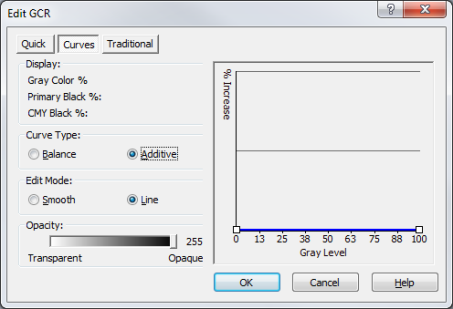
Figure 4
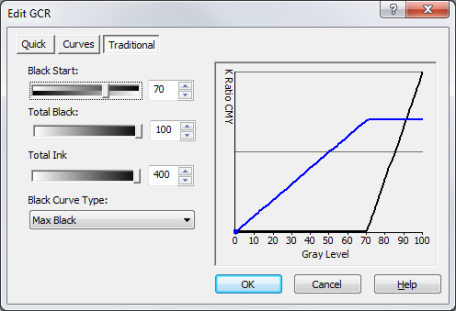
Figure 5
|




